In recent years, the threat of cyber attacks targeting critical infrastructure has become increasingly prevalent.
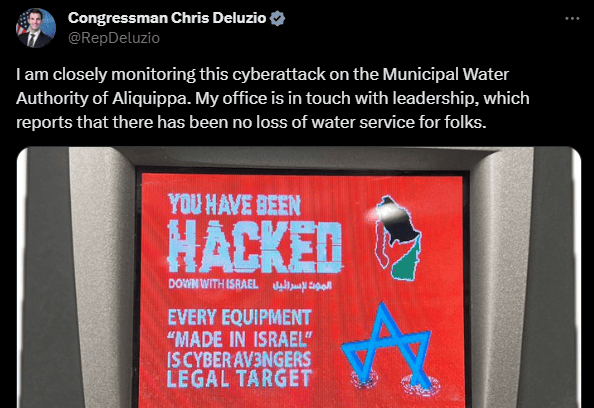
One such incident occurred in western Pennsylvania on Saturday, where the Municipal Water Authority of Aliquippa fell victim to a cyber attack by an Iranian-backed hacktivist collective known as Cyber Av3ngers.
This attack exploited the Unitronics programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used by the water authority, highlighting the vulnerabilities in our water infrastructure.
The Iranian-Backed Cyber Attack on Aliquippa’s Water Authority
The cyber attack on the Municipal Water Authority of Aliquippa involved the active exploitation of Unitronics PLCs, which are widely used in water and wastewater systems (WWS) to monitor and regulate critical processes.
Read: Iran Tells Hamas It Won’t Be Joining War Against Israel: REPORT
The attack was attributed to Cyber Av3ngers, a hacktivist collective with a history of targeting critical infrastructure. This group has previously claimed responsibility for infiltrating water treatment stations in Israel, indicating their expertise in compromising the integrity of water infrastructure.
The specific target of the attack was the booster station responsible for monitoring and regulating water pressure in Raccoon and Potter Townships.
By gaining control of the PLCs, the hackers could disrupt the water pressure, potentially impacting the supply of clean and potable water to the affected areas.
Fortunately, the water authority promptly detected the attack and switched to manual operations, minimizing the risk to the water supply.
“Attacks on our critical infrastructure like water are unacceptable. I intend to push for a full investigation here and accountability for the attackers, and I will continue the important bipartisan work on the House Armed Services Cyber, Information Technologies, and Innovation (CITI) Subcommittee to shore up America’s defenses,” Congressman Chris Deluzio in a social post.
Vulnerabilities and Implications
The cyber attack on Aliquippa’s water authority unveils several vulnerabilities in the water infrastructure sector and raises significant implications for the security of critical processes.
One of the key vulnerabilities exploited in this attack was the default password used in the Unitronics PLCs. By changing the default password, organizations can significantly enhance their protection against such attacks.
Another critical vulnerability lies in the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for access to PLCs. Implementing MFA can add an extra layer of security, making it harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access to critical systems.
Disconnecting PLCs from the internet is also crucial in preventing remote attacks. By isolating these systems from the public network, the risk of unauthorized access is significantly reduced.
Furthermore, regularly backing up the logic and configurations of PLCs is essential for fast recovery in case of a cyber attack. By having up-to-date backups, organizations can quickly restore the system’s functionality and minimize the impact of the attack on critical processes.
Additionally, applying the latest updates and patches to PLCs is vital for addressing any known vulnerabilities and ensuring the system’s overall security.
The Importance of Collaboration and Awareness
Protecting water infrastructure from cyber attacks requires collaboration and awareness within the industry. Water authorities and organizations should actively participate in information sharing initiatives such as the Water Information Sharing and Analysis Center (WaterISAC), which facilitates the exchange of cybersecurity threat intelligence.
Moreover, it is crucial for water facilities to prioritize cybersecurity training and awareness programs for their staff. By educating employees about potential risks and best practices, organizations can create a culture of cybersecurity and ensure that everyone understands their role in safeguarding critical infrastructure.
Government Initiatives and Support
Recognizing the growing threat of cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, the U.S. government has taken steps to address the issue.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) plays a crucial role in responding to cyber threats and providing guidance to organizations. Water facilities should actively engage with CISA and leverage the resources and support available to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
The government’s efforts to regulate and support the water sector’s cybersecurity have also been evident. However, challenges remain, including financial constraints faced by many smaller water utilities. It is essential for these utilities to seek assistance and guidance from industry organizations and government agencies to improve their cybersecurity capabilities.
Android Users, Click To Download The Free Press App And Never Miss A Story. Follow Us On Facebook and Twitter. Sign up for our free newsletter.
We can’t do this without your help; visit our GiveSendGo page and donate any dollar amount; every penny helps
